Pesticides, Body Chemistry and PH Balance
STOP the Poisoning
In medicine the balance of life and health all revolves around the davenport diagram that is the blood pH balance. This is a chemical equation to summarize the exchange and balance of hydrogen (pH) or the power of one, the hydrogen atom and its electron.
There is no chemical reaction possible in the absence of water (H2O). This means all chemistry in our body requires water. Water ensures the availability of electrons, the energy to bond/bind or create chemical reactions or molecules for other functions.
Neutral pH is 7.0 and at 7.0 there is x amount of oxygen in your blood. Normal is optimal pH at 7.35: At 7.35 pH the blood contains 20x more oxygen than neutral pH at 7.0. When the blood is acidic at 6.65 pH, the blood has 40x less oxygen than optimal/normal (7.35 pH).
The blood pH is an amazing, delicate balance. The body’s number one physical requirement for life is air-oxygen and is regulated by blood pH.
Primary Regulating body-systems
- The body can live for only minutes without oxygen.
- The body can live for only days without water
- The body can live for only 1-2 months without food.
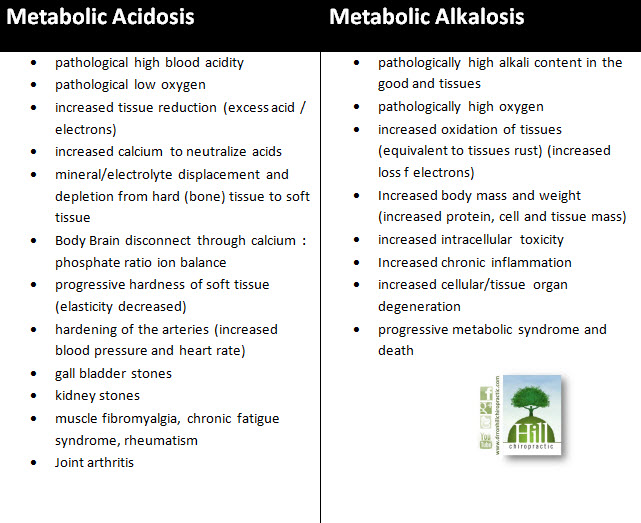
The blood pH is slightly alkaline at 7.35pH to optimally restore oxygen to all body tissues to maintain cellular metabolism. Anything that tips the pH scale to acidic or alkaline can potentially cause illness or death if too extreme. Acute exposure to elements that shift the pH balance to an extreme is an obvious poisoning.
There are four ways to poison yourself.
- Inhalation
- Absorption
- Ingestion
- Injection
Chronic low-grade exposure to elements that shift the pH balance to an extreme is not as obvious, but there are a few indicators that have been utilized by innovators.
The names for these pH shifts are called Metabolic Acidosis and Metabolic Alkalosis.
Acute signs and symptoms of poisoning are obvious.
- chemical poisoning appear in 1-30 min
- bacterial poisoning appear in 1-12 hours
- Viral and bacterial poisoning appear in 12-48 hours
Three ways to detect body poisoning
- Blood Test – Chronic organophosphate poisoning disrupts the brain neurotransmitter (nt) – acetylcholine. This can be detected medically by measuring blood cholinesterase (an enzyme to properly regulate the neurotransmitter acetylcholine)
- Heart Rate Variability Test – In heart rate variability measurements, acetylcholine is a parasympathetic nerve (PNS) neurotransmitter. Parasympathetic nerve disruption / dysfunction may appear as depletion of the body’s health reserve: The gas tank is empty.
- Allergy, skin and breathing symptoms – Clinical phosphate exposure, in either food or the environment is detected immediately in the body, by your blood antibodies…This is an allergy response and maybe expressed in numerous ways: lungs, sinus, breathing, skin and rashes – itching, etc; nerves, and restlessness, anxiety, fidgeting, twitching, staring, vocal difficulties, laryngitis, ADD and brain dysfunction, emotional dysfunctions; digestive organ troubles / pain; immune dysfunction and illness; reproductive and kidney problems and others.
Long term consequences of chronic organophosphate poisoning and resultant ‘body burden’
- Deficits in cognitive and psychomotor function
- Decreased vibration sensitivity
- Impaired nerve conduction
- Stomach, brain (male), uterine (female), confer and non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma.
- Short term exposures are managed better than the long-term
Antibodies detect whether a protein is phosphorylated at a particular site. That is why so many varied symptoms appear with phosphate sensitive (poisoned) people.
The study of phosphorylated proteins is called Phosphoproteomics. This is a sub-branch of a mass spectrometry-based study called Proteomics.
Eugene P Kennedy described the first ‘enzymatic phosphorylation of proteins.
 There are nine known major regulatory body-systems that are negatively disrupted by protein phosphorylation. The range of dysfunction and body interference is mind-boggling.
There are nine known major regulatory body-systems that are negatively disrupted by protein phosphorylation. The range of dysfunction and body interference is mind-boggling.
- Body Temperature – Biological thermodynamics (body heat and energy).
- Cell Function – Sodium: Potassium cell membrane transport (cell and body vitality)
- Enzyme Function
- Insulin Function – Insulin signaling pathway
- Tyrosine amino acid metabolism
- Thyroid hormone production à metabolism
- Dopamine (nt) for brain function: love pleasure, learning, cognitive ability and psychomotor function
- Stress hormone production: Neurotransmitters – Catecholamine, Norepinephrine/noradenaline, Epinephrine/adrenaline
- Immune system– Protein-protein interaction “recognition domains”
- Phagocytic cell function– process of the body’s ability to repair and replace it’s cells
- Waste management– Protein degradation (body’s ability to repair and replace itself)
- Body protection/self-defense – Body targets the proteins tagged for destruction (body’s ability to repair and replace itself)
Phosphorylation turns many enzymes (receptors/proteins) off/on. There are 200,000 articles on Medline database describing 500 human enzymes affected.
The most common amino acids affected are:
- Serine
- purines, pyrimidines (DNA)
- amino acids – glycine, cysteine, tryptophan, sphingolipids
- folate, chymotrypsin, trypsin (digestive enzymes)
- Threonine
- for Kreb cycle (energy-production)
- pyruvate, acetyl CoA, glycine
- Tyrosine (Tyrosine, phenylalanine, tryptophan-antidepressant)
- synthesize protein from casein (egg)
- precursor for dopamine
- precursor for thyroid
- precursor for alkaloid (morphine)
- precursor for phenols (coumarin)
- precursor for skin pigment (melanin)
- Histidine
- precursor synthesize for histamine (allergy)
- precursor for carnosine (zinc healing, digestion, decreased carbon dioxide in the blood)
- precursor for ammonia (kidney function)
- precursor for urocaric acid (urea/nitrogen excretion)
- precursor for master antioxidant (ergothioneine)
- precursor for succinate dehydrogenase (mitochondria function)
- Arginine
- precursor for mRNA
- precursor for no-nitric oxide
- increased immune function, increased vasodilation and increased blood flow
- decreased Nitric Oxide: increased atherosclerosis, diabetes, hypertension | decreased sexual function
- Lysine
- precursor for elastin and collagen
- precursor for building block for all protein
- precursor for major role in calcium absorption
- precursor for building muscle (protein)
- precursor for repair/recovery from injuries, surgery
- precursor for production of hormones, enzymes, antibodies
- decrease lysine, increase serotonin uptake
- decrease lysine, increase anxiety, increase immune deficiency
Consider an “ALLERGY” (hypersensitivity/intolerance, etc) as the body immediately and reliably telling you that you are being “POISONED”. Allergies are your antibodies at work to give you signs and symptoms to make you aware of your body’s environmental situation.
Progressive dysfunction to disability, generation after generation: give your body a chance, give your children and hopefully grandchildren a chance…STOP the Poisoning…Today.
Beware what you breathe, drink and eat…sow simple!